
The index of refraction is a constant for each material and is greater than one when light enters a denser medium from a rarer medium as from air through a liquid. When light traverses from air through a liquid, its index of refraction is the ratio of the sine of the angle of incidence to the sine of the angle of refraction. Swanson, in Adhesives Technology for Electronic Applications (Second Edition), 2011 7.1.7 Index of refraction The shading area for the rectangular solar pond is defined as θ h is the hour angle which θ h is equal to zero while the sun is at the highest point in the sky at 12 pm and its value in the morning becomes positive (+) and also in the afternoon becomes negative (−). We use 35☁8′ East longitude and 36★9′ North latitude for the location of the system at the Cukurova University in Adana, Turkey.
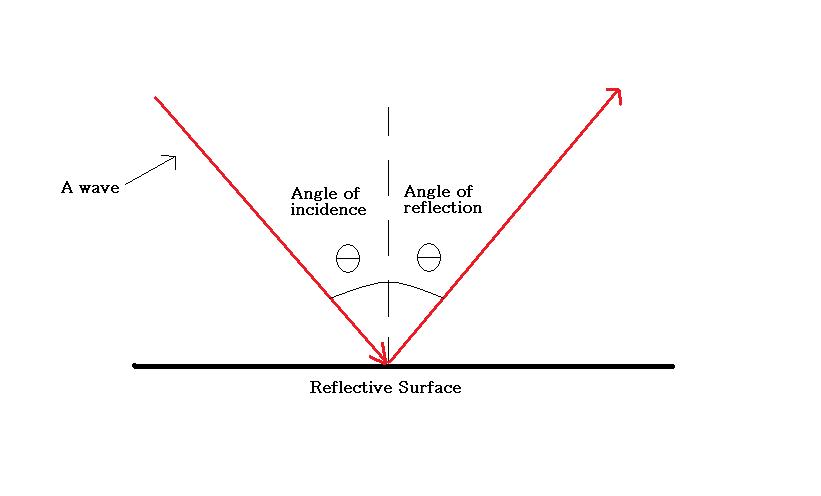
#Angle of refraction vs angle of reflection plus#
(φ) is calculated according to latitude angle that is defined as −90<(φ)<+90, which is the solar elevation angle and has a plus sign for the Northern hemisphere and a minus sign for the Southern hemisphere. Here δ d is declination angle which can generally be calculated by the Cooper equation as δ d=23.45sin. The angle that the refracted ray makes with the normal line, which is called the angle of refraction, defined by the Snell law as θ rf=sin −1(1.33sinθ i), where θ i is called the incidence angle, which is equal to the zenith angle (θ z), is the angle between the normal of the surface of the solar pond and incident solar radiation and is defined as θ z=cos −1. But what can we pull out of this brief discussion for useful design purposes?
#Angle of refraction vs angle of reflection full#
Now, being that many of the places that humans live in experience something less than a clear day, estimating the diffuse component is challenging, and full of uncertainties. 22 After review, all models appear to have a regional character associated with seasons, clouds, air mass source regions-regional characters that we known as synoptic, mesoscale, and microscale weather (or meteorology). Muneer has investigated several of these diffuse sky models. That at least is a simple geometric matter of Eq. One can directly measure the total downwelling irradiance, and project the DNI data onto beam irradiance on a horizontal plane. Or can we? As it turns out, the approximation of diffuse irradiance is a non-trivial pursuit. Having explored the earlier model for the DNI beam normal component ( G b, n) and the beam component for horizontal surfaces in the shortwave band, we can move on the diffuse horizontal irradiance (DHI) calculation. Notice the exponential form of both equations, and compare how Hottel was able to generate a somewhat useful model of a clear sky just by using the principle of transmittance.
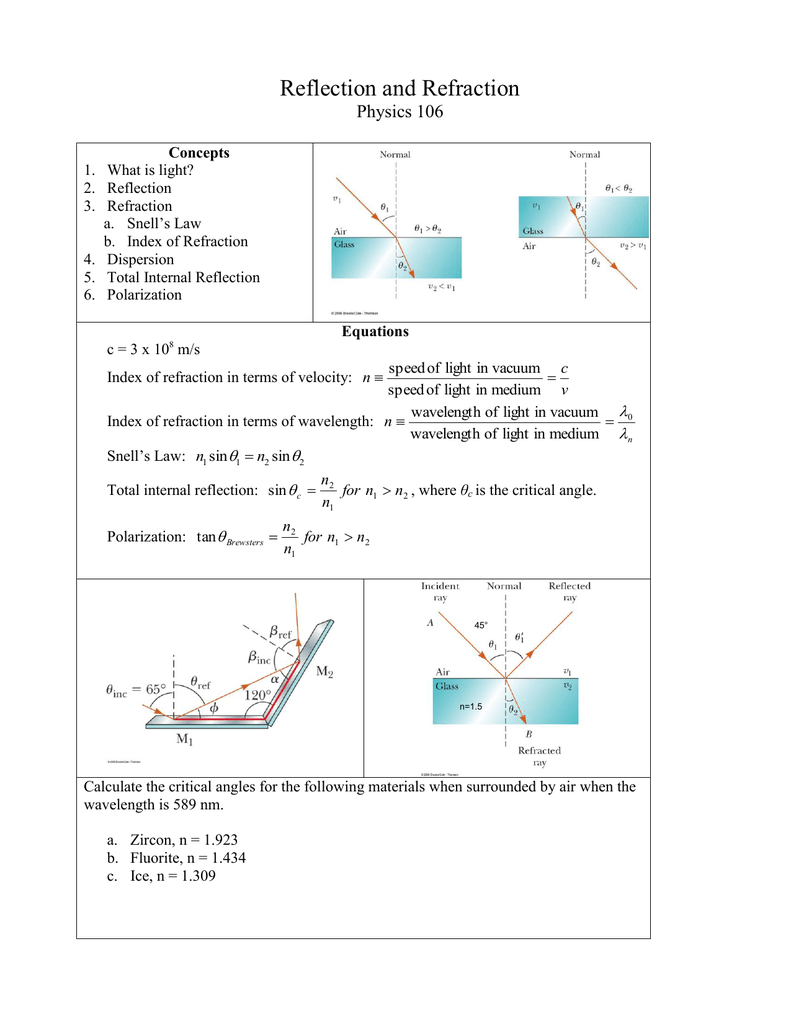
(5.36) (refraction is assumed to be very small here). (5.35) has nearly the same meaning as the angle of refraction in Eq. For transparent cover materials the extinction coefficient will be on the order of 4–30 m −1. Extinction coefficients in solar energy tend to be reported within the shortwave band as inverse distances, and so by multiplying by a distance one results in a dimensionless numerator (as Hottel indicated). The value of τ α can be calculated by knowing the angle of refraction ( θ 2) and the extinction coefficient of the material ( k), as well as the thickness of the material or distance that light must propagate through ( d).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
